
There is a more rigorous way to do it using Group Theory. In short, count the orbitals from left to right in the list above until you have the same number of orbitals as the number of electron groups. So, we assume the hybridization is #s+p+p -> color(blue)(sp^2)#. Or, in #"BH"_3#, three #"B"-"H"# bonds are made, and there are no other lone pairs or bonds. (You can think of it as the central atom "anticipating" future bonds it can possibly make.) #s, p, p, p, d, d, d, d, d, f, f, f, f, f, f, f#įor example, in #"NH"_3#, three #"N"-"H"# bonds are made and one lone pair of electrons is leftover, so we assume that the hybridization is #s+p+p+p -> color(blue)(sp^3)#. For general chemistry, we just count the number of electron groups around the central atom, and assume that the orbitals used are in order of angular momentum #l#. What is hybridization state of benzyl carbonium?.Hybridization of carbon in diamond, graphite, and ethyne is?.Which is incorrect about hybridization?.State the hybridisation on 5 carbon atoms of the given molecule.Find the incorrect statement n hybridization.What is the hybridization of carbon in fullerene.Calulate the number of bonds made by Sulphur atoms.Number of sp 2 hybrid orbitals in benzene.sp 3d 2 hybridization is not displayed by?.The hybridization of oxygen in oxygen peroxide is?.What is the hybridization of boron in diborane?.Correct geometry and hybridization of XeF 4 is?.sp 3d 2 Hybridization: one s orbital, three p orbitals, and two d orbitals intermix to form six sp 3d 2 hybridized orbitals.sp 3d Hybridization: one s orbital, three p orbitals, and one d orbital intermix to form five sp 3d hybridized orbitals.sp 3 Hybridization: one s orbital and three p orbitals intermix to form four sp 3 hybridized orbitals.sp 2 Hybridization: one s orbital and two p orbitals intermix to form three sp 2 hybridized orbitals.sp Hybridization: one s orbital and one p orbital intermix to form two sp hybridized orbitals.Based on the type of orbitals, hybridization can be classified into sp, sp 2, sp 3, sp 3d, sp 3d 2, and sp 3d 3.
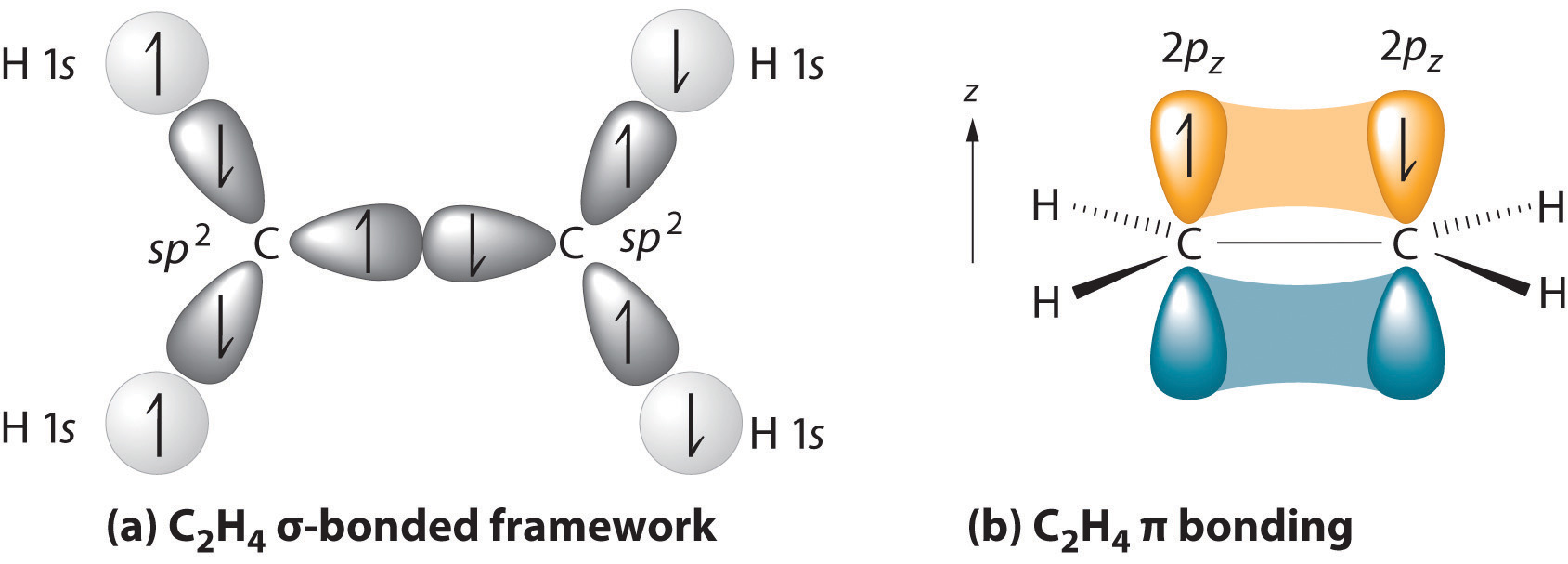

Only atomic orbitals with equal energies undergo hybridization.Some interesting features of hybridization are listed below: Based on the type of orbitals, the hybridization can be labeled as sp, sp 2, sp 3, sp 3d, sp 3d 2, and sp 3d 3.During the process of hybridization, the atomic orbitals of equivalent energy such as two ‘s’ orbitals or two ‘p' orbitals or ‘s’ orbital with a ‘p’ orbital or ‘s’ orbital with a ‘d’ orbital are intermixed to form hybridized orbitals.The theory of Hybridisation is an extension of the Valence bond theory which helps us to understand the characteristics of the bond parameters such as bond order, bond length, bond angle, etc.This intermixing is primarily based on quantum mechanics.There is minimum repulsion between these hybridized orbitals. When two or more atomic orbitals of different shapes but identical energy levels re-distribute themselves to form hybrid orbitals that have a slightly different shape, equivalent energy levels, and orientations, it is called hybridization or hybridisation. Key Terms: Hybridization, sp, sp 2, sp 3 Hybridization, Atomic Orbitals, Valence Bond Theory, Bond Angle, Molecular Orbital Theory


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
